The Curious Mouse's Guide to Zambia's 2025 National Budget
4 OCTOBER 2024 : 12:00AM
Gerald Hamuyayi
Zambia's government unwrapped its 2025 National Budget, with a primary focus on economic recovery and promoting inclusive growth under the theme "Building resilience for inclusive growth and improved livelihoods." The budget, presented by the Ministry of Finance and National Planning, Dr Situmbeko Musokotwane outlined ambitious targets and fiscal reforms aimed at stabilising the economy and improving the lives of Zambians. This is the fourth budget of the Hichilema’s lead UPND administration in their five-year governance mandate elapsing in 2026.
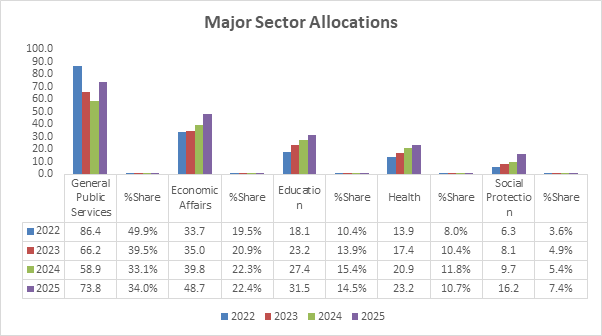
Zambia's 2025 budget is projected to be K217 billion, representing a 22% increase over the 2024 budget and a 9.3% rise above the forecast 2024 budget outturn of K198.6 billion. The revenue streams for this budget comprise taxes, non-tax revenues, natural resource revenues, and both domestic and foreign funding assistance. In terms of expenditures, key allocations are directed towards social and economic sectors, governance, and infrastructure. Notably, the economic and social sectors have seen a consistent increase in budget share, while other sectors have experienced marginal fluctuations as highlighted in the "Major Sector Allocations" histogram.
The Zambian government presented what a majority of analysts describe as an ambitious 2025 budget aiming to achieve a GDP growth rate of 6.6% real GDP growth, a significant shift from the projected 2.3% at end of 2024. This growth is to be driven by key sectors such as mining, agriculture, and information and communication technology. To further support this growth, the government targets to increase domestic revenue to at least 21.4% of GDP while reducing the fiscal deficit to 3.1% of GDP.
Speaking at the KPMG Zambia Budget Analysis, Mr. Yosuf Dodia's comments resonated with many Zambians: "The first thing that struck me was the ambitious target to raise K174 billion from taxes and domestic revenues. This amount is equivalent to the entire 2024 national budget. In other words, if we succeed in raising K174 billion in 2024, we would be funding the budget 100% from domestic resources without borrowing." Notably, the government's macroeconomic objectives lack a definitive inflation target, instead aiming to "Reduce inflation to the 6-8 percent target band in the medium-term." For context, a trip down memory lane indicates that Zambia last achieved a below 8% inflation rate in 2018.
Debt Management and Economic Growth
Another focus of the 2025 budget is debt management, having restructured US$11.76 billion of the US$13.34 billion of its external debt under the G-20 common framework. The restructure has created fiscal space, allowing for enhanced investment in critical sectors and social programs. On the downside, the resumption of debt service on the restructured debt has ballooned the interest and principal by 177.2% from K6.0 billion in 2024 to K16.7 billion in 2025. This enormous debt repayment accounting for 7.7% of the 2025 budget will be a source of currency and inflationary spill over pressures. Domestic debt services stand at K37.3 billion for the 2025 fiscal year.
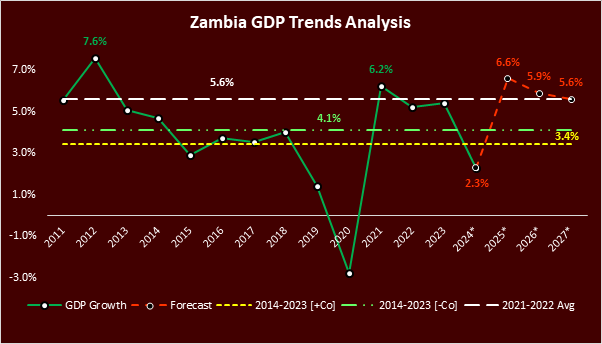
Zambia's projected 6.6% GDP growth rate for 2025 has sparked an attainability debate among commentators and analysts, as it would be Zambia's highest growth rate since the 7.9% growth rate recorded in 2012. Historical trend analysis reveals a 10-year average GDP growth rate of 4.1% and 3.4%, excluding and including the Covid-19-induced contraction year of 2020. The 2025 target is just one percentage point above the 5.6% growth average achieved from 2021 to 2023. To achieve this ambitious goal despite Zambia’s economic headwinds, significant progress is needed in key sectors, including mining, agriculture driven by favourable precipitation forecasts, and electricity generation.
A Bet on Primary Industry for Growth

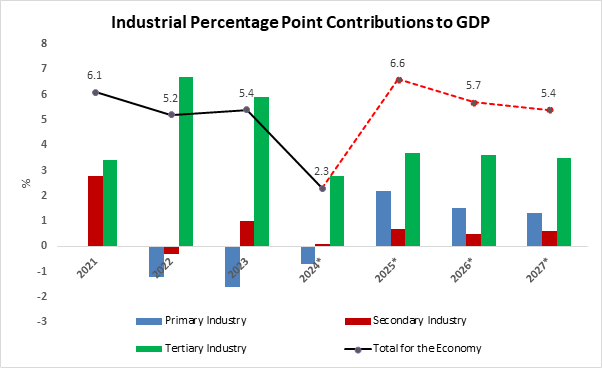
Zambia's primary industry, comprising mining and agriculture, is expected to drive GDP growth, according to Secretary to the Treasury Mr. Felix Nkulukusa's presentation at the Ministry of Finance symposium and KPMG Zambia 2025 Budget Analysis Forums. This sector is projected to contribute around 2.2 percentage points to the forecast 6.6% GDP growth in 2025, surpassing its 10-year high of 1.87 percentage points in 2020, largely due to elevated copper prices.
The industry's growth is a dramatic reversal of its lacklustre performance between 2021 and 2023, which had actually subtracted from economic growth. The 'Industrial Percentage Point Contributions to GDP' graph illustrates how different industrial sectors have contribute to GDP, alongside government forecasts.
Realising Zambia’s Copper Dream
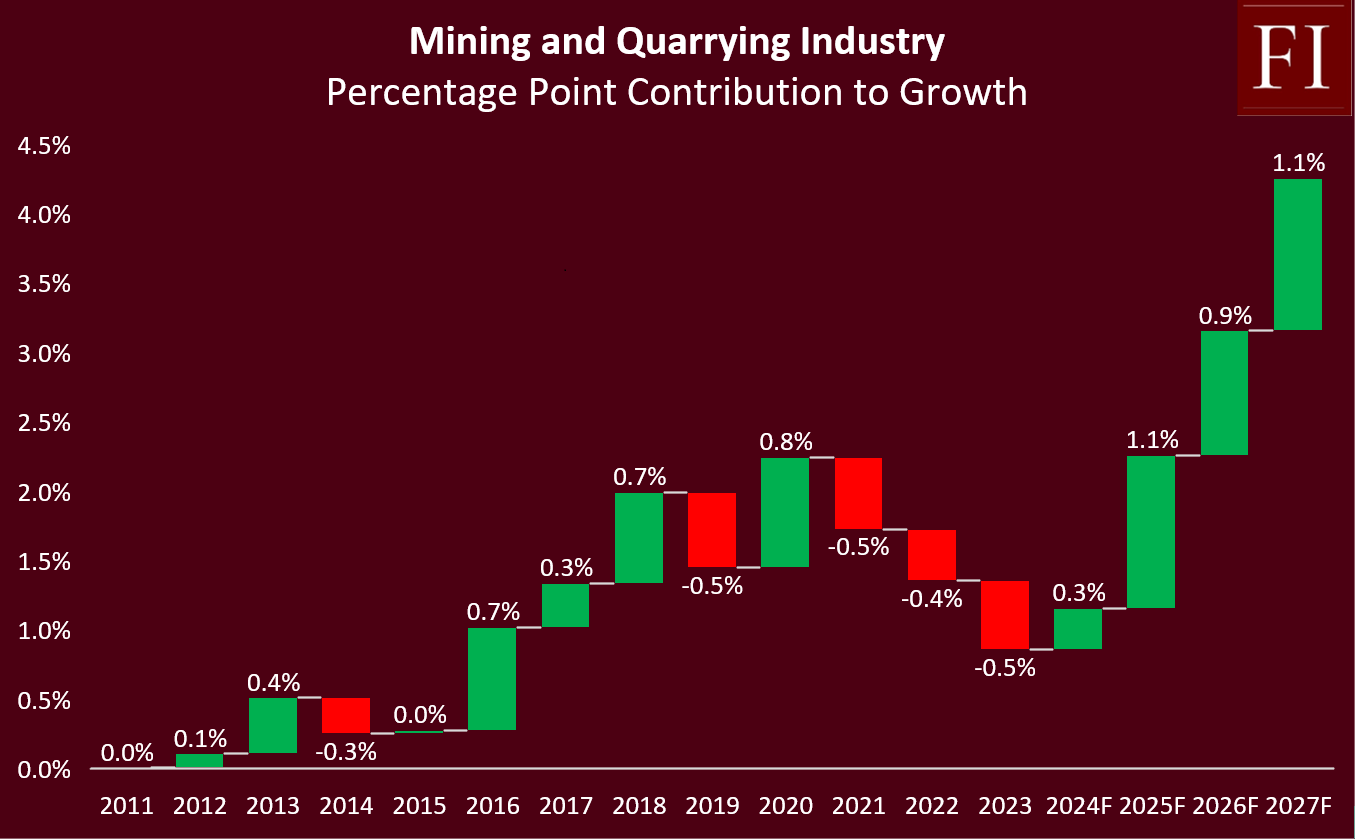
The 2025 budget includes a significant increase in funding for geological mapping, from K160 million to K364 million, aimed at enhancing mineral discovery, mining investment, and ultimately, mining output in the medium to long term. Although short-term mining output relies on existing operating mines with minimal additions from new mines, Hakainde Hichilema's administration targets a historical turnaround, seeking unprecedented positive contributions to growth of approximately 1.1% in 2024, 0.9% in 2026, and 1.1% in 2027. This goal is a stark shift from industry's historical performance, having stagnated despite accounting for 9.7% of real GDP over the past five years. In addition, the industry negatively contributed to GDP growth in four of the last five years, as illustrated in the "Percentage Point Contribution of Mining and Quarrying Industry to Growth" chart.
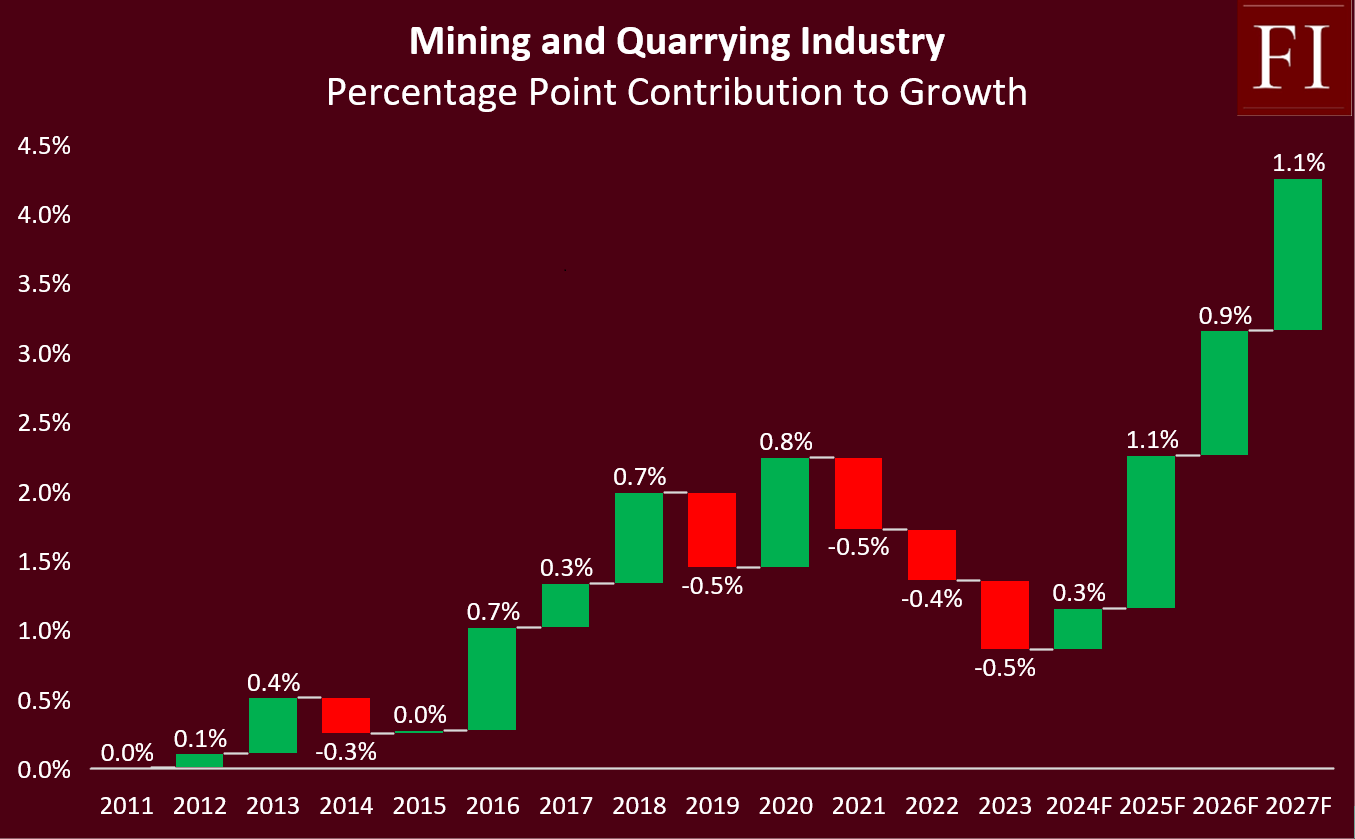
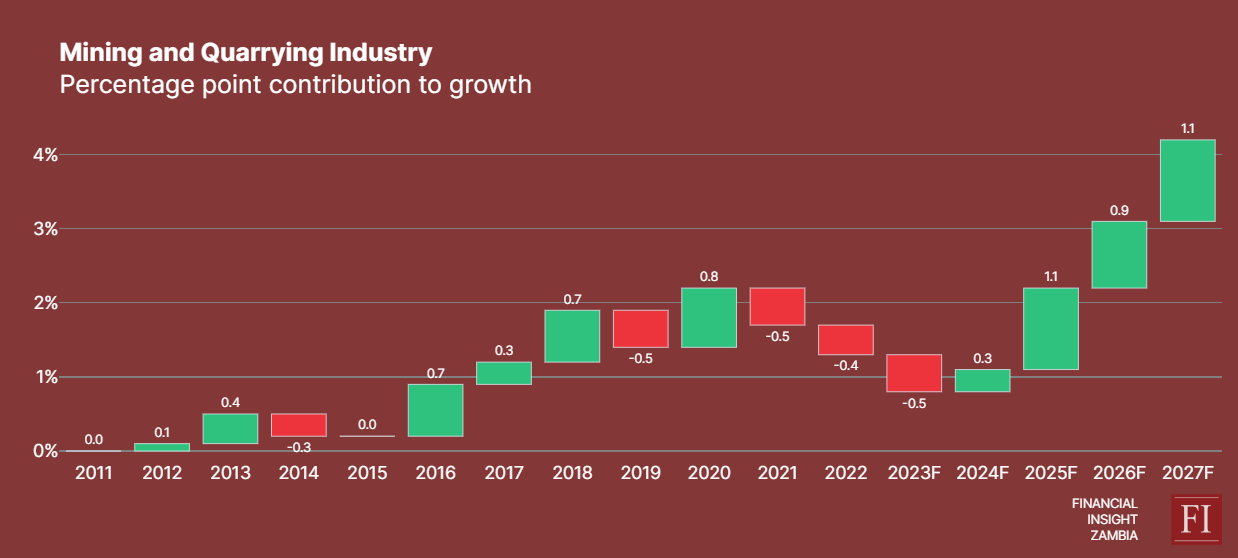
With the government having troubleshot troubled assets such as Mopani and Konkola Copper Mine, Zambia's mining sector is set for revitalisation. This move is expected to improve the mining investment climate, encourage exploration, and increase copper production, which is crucial for Zambia's economy. As the largest contributor to Zambia's tax revenue and accounting for more than 65% of total export earnings, the sector's expansion is extremely important.
Concerningly, the secondary industry's contribution is expected to fall short of its 2021-2023 average of 1.2 percentage points. Despite support through multifacility economic zones and increased access to finance for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) via the expanded Credit Guarantee Scheme, which received K852 million in funding - more than double its 2024 budget allocation. The forecast recovery in the primary industry has not been matched by corresponding growth in secondary industries, indicating that significant value from primary industries will remain unadded. This deficiency in value addition hampers optimal employment creation in the secondary industry, limiting its potential to reduce unemployment by absorbing Zambia’s widening labour supply.

Investing in Zambia's Future
The 2025 budget prioritises social protection programs, allocating significant resources to safeguard vulnerable groups, aiming to reach over 2.5 million households and benefit more than 13.9 million individuals. Notably, social program allocation has increased by 67%, with the social cash transfer doubling from K4.1 billion to K8.3 billion. To mitigate drought effects, the government has introduced a Cash for Work program, allocating K2.0 billion to pay citizens for community work. Investments in education and health will remain a priority, with plans to recruit 2,000 new teachers and 2,000 additional health workers, while also focusing on the construction and rehabilitation of essential learning infrastructure.
The Constituency Development Fund (CDF) has been enhanced, promoting decentralised decision-making and empowering local communities. Additionally, the government plans to transition the Farmer Input Support Programme to an e-voucher system, improving efficiency and eliminating ghost farmers. Other positive macroeconomic indicators include the increasing gross international reserves to US$3.9 billion, representing approximately 4.3 months of import cover. The ICT sector is expanding, with increased mobile subscriptions and the entry of new operators like Zed Mobile and Starlink.
Zambia's 2025 budget presents an optimistic outlook despite present troubles. The drought and current energy crises have taken a disproportionate toll on livelihoods, significantly exacerbating the struggles of vulnerable populations. Furthermore, the country faces economic headwinds, including rising inflation rate of 15.6% as of September 2024, alongside exchange rate depreciation. A lot of hard work and interplay from the monetary, fiscal and private sector will be required to achieve the envisioned macroeconomic targets.
References
2025 Budget Speech
Zambia Statistics Agency
https://www.zamstats.gov.zm/economic-statistics-tables/
Secretary to the Treasury 2025 Budget Analysis Presentation
https://web.facebook.com/share/v/RDnWbcx6SWqxWsy5/
2025 Budget Analysis by Secretary to the Treasury
Featured Image
2024-10-04
Category: Economic & Business Sectors